research target:miR-149,hepatocellular carcinoma
Periodicals:Oncotarget
IF:5.168
Cooperative Unit:Army Medical University,UCSF School of Medicine
Time of publication:October,2015

Summary
microRNAs have been implicated in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) metastasis, which is predominant cause of high mortality in these patients. Although an increasing body of evidence indicates that miR-149 plays an important role in the growth and metastasis of multiple types of cancers, its role in the progression of HCC remains unknown. Here, we demonstrated that miR-149 was significantly down-regulated in HCC, which was correlated with distant metastasis and TNM stage with statistical significance. A survival analysis showed that decreased miR-149 expression was correlated with a poor prognosis of HCC as well. We found that over-expression of miR-149 suppressed migration and invasion of HCC cells in vitro. In addition, we identified PPM1F (protein phosphatase, Mg2+/Mn2+-dependent, 1F) as a direct target of miR-149 whose expression was negatively correlated with the expression of miR-149 in HCC tissues. The re-expression of PPM1F rescued the miR-149-mediated inhibition of cell migration and invasion. miR-149 regulated formation of stress fibers to inhibit migration, and re-expression of PPM1F reverted the miR-149-mediated loss of stress fibers. Moreover, we demonstrated that over-expression of miR-149 reduced pMLC2, a downstream effector of PPM1F, in MHCC-97H cells. In vivo studies confirm inhibition of HCC metastasis by miR-149. Taken together, our findings indicates that miR-149 is a potential prognostic biomarker of HCC and that the miR-149/PPM1F regulatory axis represents a novel therapeutic target for HCC treatment.
Keywords: hepatocellular carcinoma, miR-149, metastasis, PPM1F, microRNA
Research Background
Many reports have shown that the deregulation of miRNAs is involved in the growth and metastasis of HCC. For example, upregulation of miR-182 is related to intrahepatic metastasis and poor prognosis, whereas a decrease in miR-124 is significantly associated with a more aggressive phenotype and poor prognosis. miR-149 primarily functions as an anti-tumor miRNA, and its expression is deregulated in multiple types of cancers, including breast cancer , colorectal cancer (CRC), gastric cancer ,head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) and non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) .
In this study, we demonstrate that miR-149 is frequently down-regulated and significantly correlates with tumor metastasis and poor prognosis in HCC patients. We further proved that miR-149 inhibited the metastasis of HCC in vivo and in vitro by suppressing actin-regulatory proteins PPM1F.
Partial results of cooperation
Figure 1: miR-149 is frequently down-regulated in human HCC tissue and associated with poor clinicopathologic features and a low postoperative survival rate.
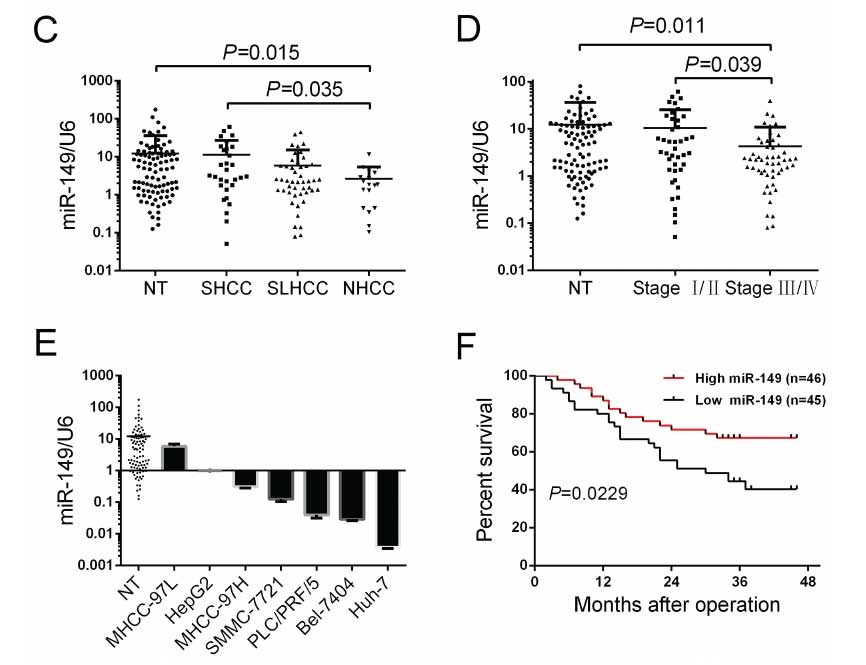 Figure 2: Exogenetic over-expression of miR-149 suppresses HCC cell migration and invasion in vitro.
Figure 2: Exogenetic over-expression of miR-149 suppresses HCC cell migration and invasion in vitro.
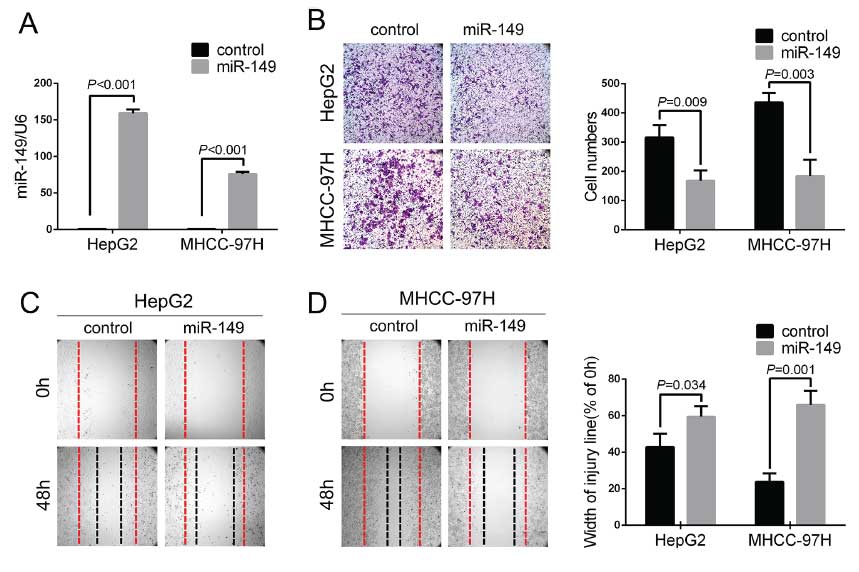 Figure 3: miR-149 down-regulates PPM1F expression by directly targeting its 3′-UTR.
Figure 3: miR-149 down-regulates PPM1F expression by directly targeting its 3′-UTR.
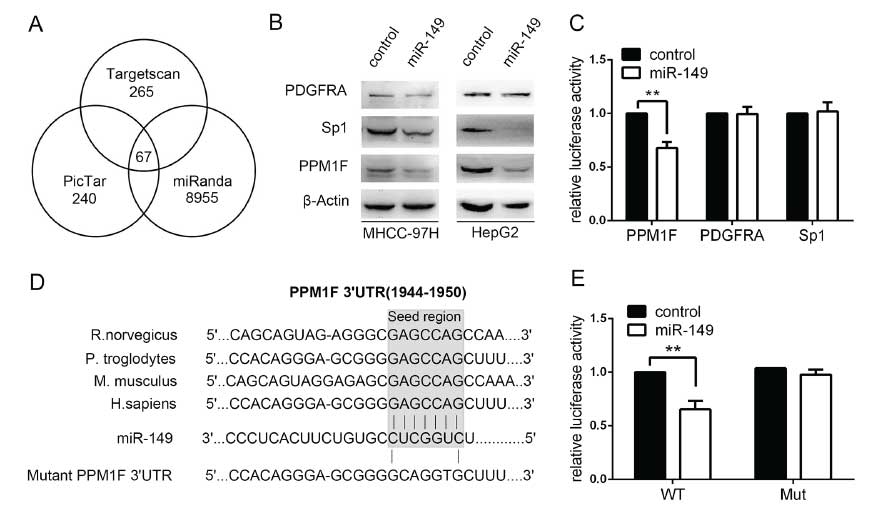 Figure 4: PPM1F is frequently up-regulated and inversely associated with the expression of miR-149 in HCC.
Figure 4: PPM1F is frequently up-regulated and inversely associated with the expression of miR-149 in HCC.
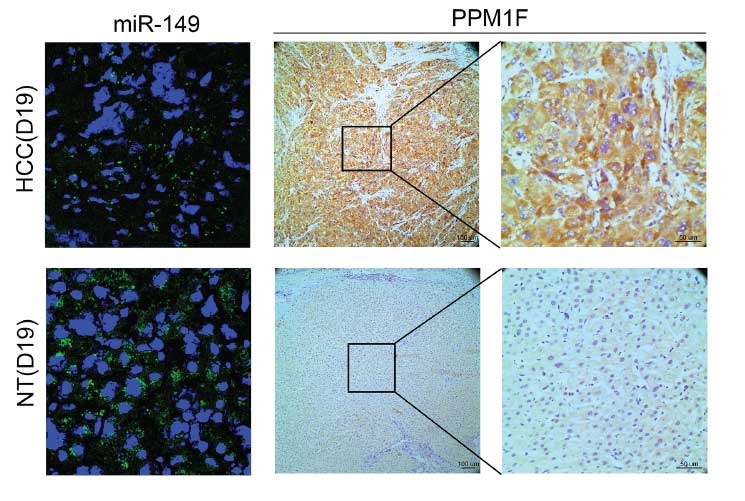 Figure 5: PPM1F rescued the effect of miR-149 on the invasion and migration of HCC cells.
Figure 5: PPM1F rescued the effect of miR-149 on the invasion and migration of HCC cells.
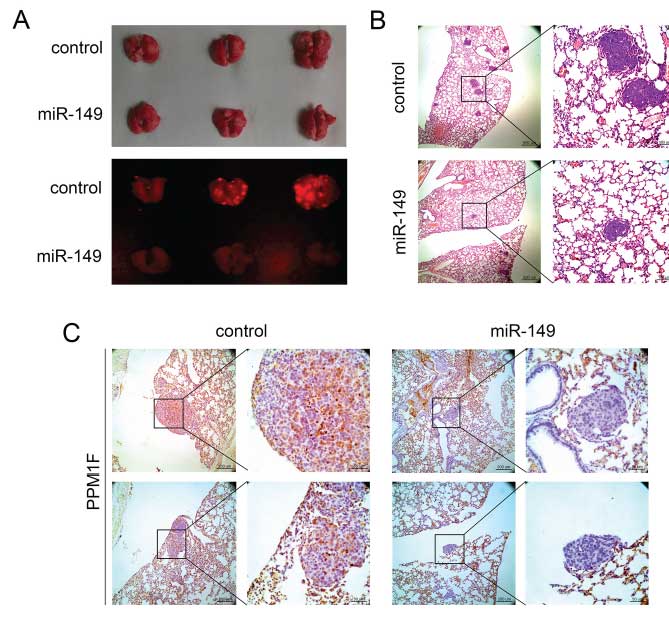
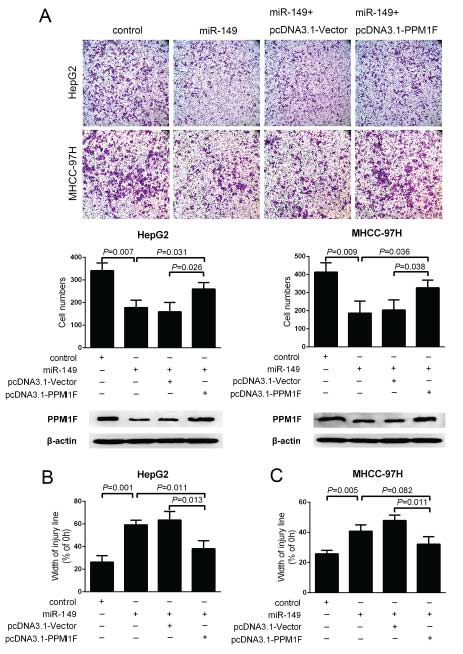 Figure 6: miR-149 suppresses HCC metastasis in vivo.
Figure 6: miR-149 suppresses HCC metastasis in vivo.
References
Gang L, Ya-Ling C, Bo T, et al. miR-149 represses metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting actin-regulatory proteins PPM1F[J].
Oncotarget, 2015, 6(35):37808-23.
BersinbioTM cooperative technology:FISH
Original link:http://europepmc.org/backend/ptpmcrender.fcgi?accid=PMC4741967&blobtype=pdf






