research target:FOXO1; breast cancer; cancer stem cells; miR-5188; stemness; timeless; ubiquitination; β-catenin.
Periodicals:Mol Ther
IF:11.450
Cooperative Unit:Southern Medical University
Time of publication:August, 2019
 Summary
Summary
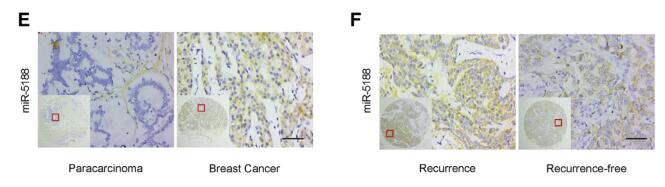
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) play an essential role in the self-renewal of breast cancer stem cells (BCCs). Our study aimed to clarify the role of proto-oncogene c-Jun-regulated miR-5188 in breast cancer progression and its association with Timeless-mediated cancer stemness. In the present study, we showed that miR-5188 exerted an oncogenic effect by inducing breast cancer stemness, proliferation, metastasis, and chemoresistance in vitro and in vivo. The mechanistic analysis demonstrated that miR-5188 directly targeted FOXO1, which interacted with b-catenin in the cytoplasm, facilitated b-catenin degradation, and impaired the nuclear accumulation of b-catenin, thus stimulating the activation of known Wnt targets, epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) markers, and key regulators of cancer stemness. Moreover, miR-5188 potentiated Wnt/ b-catenin/c-Jun signaling to promote breast cancer progression. Interestingly, c-Jun enhanced miR-5188 transcription to form a positive regulatory loop, and Timeless interacted with Sp1/c-Jun to induce miR-5188 expression by promoting c-Jun-mediated transcription, which further activated miR-5188-FOXO1/b-catenin-c-Jun loop and facilitated breast cancer progression. Importantly, miR-5188 was upregulated in breast cancer and was positively correlated with poor patient prognosis. This study identifies miR-5188 as a novel oncomiR and provides a new theoretical basis for the clinical use of miR- 5188 antagonists in the treatment of breast cancer.
Key words: FOXO1; breast cancer; cancer stem cells; miR-5188; stemness; timeless; ubiquitination; β-catenin.
Partial results of cooperation


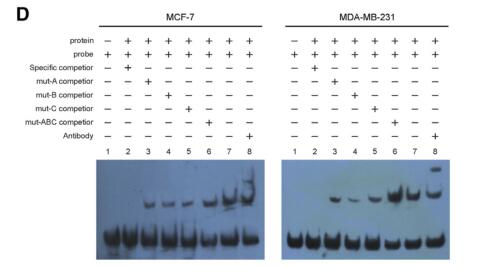 BersinbioTM cooperative technology:EMSA 、CISH
BersinbioTM cooperative technology:EMSA 、CISH
Original link:10.1016/j.ymthe.2019.08.015




